The State of Rural Healthcare
Rural healthcare continues to be a pressing issue in many parts of the world. It is a complex facet of public health policy that requires constant attention and innovation to ensure that everyone, regardless of where they live, has access to quality healthcare. Access to healthcare in rural areas is a challenge due to several factors such as distance, scarcity of healthcare providers, and lack of transportation. In rural communities, patients often have to travel great distances to receive care, which can lead to delayed or forgone care.
This lack of access to healthcare services can have serious implications for the health of rural populations. Chronic diseases can go unchecked, and preventive services may be underutilized. These challenges necessitate a rethinking of how healthcare is delivered to rural populations.
Lire également : How to Implement a Green Roof System in Urban UK Buildings?
The Rise of Telemedicine
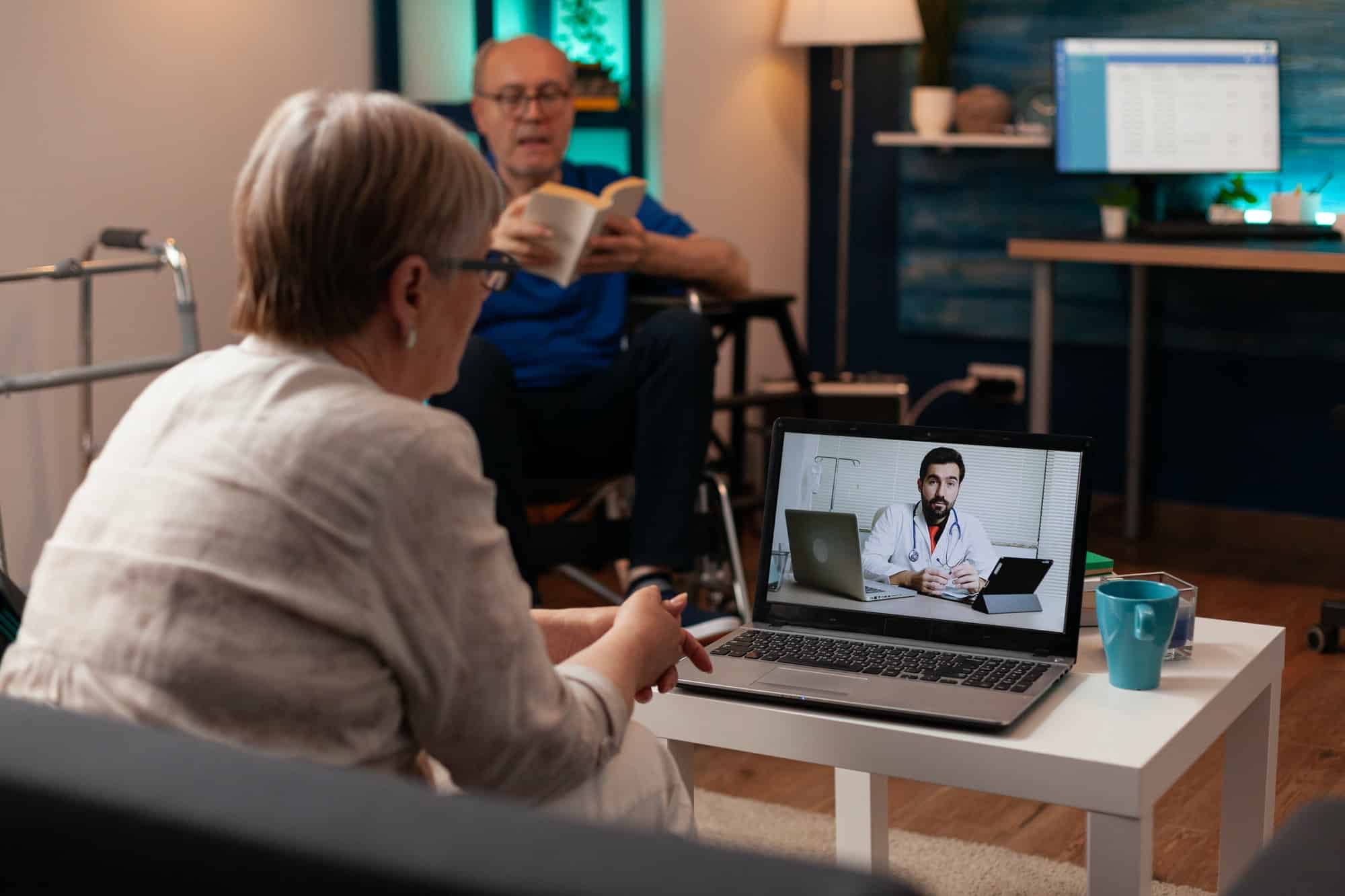
The advent of telemedicine has ushered in a new era of healthcare delivery, particularly for rural communities. Telemedicine refers to the use of technology to provide healthcare services remotely. This can be in the form of virtual visits where a patient interacts with their healthcare provider through a video call, or remote patient monitoring, where healthcare providers can track their patients’ health data from a distance.
Telemedicine has the potential to bridge the gap in rural healthcare access by allowing patients to receive care from the comfort of their homes. It eliminates the need for long travel times and reduces the associated costs. Moreover, telemedicine can help to offset the shortage of healthcare providers in rural areas by allowing providers from urban areas to offer their services remotely.
A voir aussi : What Are the Effective Ways to Reduce Food Waste in UK’s Restaurant Industry?
The Impact of Telehealth Policy
Policy plays a crucial role in facilitating the use of telemedicine in rural healthcare. Telehealth policy refers to the regulations and laws that govern the use of telehealth services. These may include policies on reimbursement for telehealth services, licensing requirements for telehealth providers, and regulations on the type of services that can be provided through telehealth.
State governments and healthcare organizations must work together to develop policies that promote the use of telemedicine in rural areas. This includes ensuring that telehealth services are covered by insurance, and that providers are adequately trained and licensed to provide telehealth services. By creating a supportive policy environment, states can help to facilitate the integration of telemedicine into rural healthcare systems.
Implementing Telehealth Programs in Rural Areas
Implementing telehealth programs in rural areas is no small feat. It requires careful planning, coordination, and investment in technology and infrastructure. Furthermore, it requires buy-in from various stakeholders including healthcare providers, patients, and the wider community.
Key steps in implementing a telehealth program in a rural area include assessing the healthcare needs of the community, selecting the appropriate telehealth technologies, training providers and patients in the use of these technologies, and continuously monitoring and evaluating the program to ensure it is meeting the needs of the community.
Telehealth and the Future of Rural Healthcare
The role of telemedicine in improving rural healthcare access is undeniable. As technology continues to advance, the scope and impact of telehealth services are likely to grow. However, it is important to note that telemedicine is not a panacea for the challenges faced by rural healthcare.
While telemedicine can provide a valuable avenue for delivering healthcare in rural areas, it should be seen as one part of a broader strategy to improve rural healthcare access. Other strategies may include recruiting and retaining more healthcare providers in rural areas, improving transportation services for patients, and investing in health education and preventive services for rural communities.
In conclusion, telemedicine holds great promise for improving rural healthcare access. However, to fully realize this potential, it will be crucial to address the various barriers to telemedicine adoption and to ensure that telemedicine services are integrated smoothly and effectively into rural healthcare systems.
Utilizing Google Scholar for Telehealth Research
Google Scholar is a vital tool in the understanding and further exploration of telehealth services in the rural healthcare system. It is a freely accessible search engine that allows scholars, researchers, and policy makers to hunt for scholarly literature across various disciplines and sources. When it comes to rural healthcare, Google Scholar can provide a wealth of knowledge on existing studies and results on telemedicine rural practices.
Researchers can use Google Scholar to access a wide variety of publications on the use of telemedicine in rural areas. This includes studies on its effectiveness, the barriers to its implementation, its benefits for patients and health care providers, and its impact on the management of chronic disease. These resources can provide critical evidence to inform policy decisions and guide the implementation of telehealth programs in rural areas.
A recent search on Google Scholar for "rural telehealth" returned over 20,000 results, highlighting the growing body of research on this topic. As the Covid pandemic has demonstrated, telemedicine has become an increasingly important tool in the delivery of healthcare services, particularly in rural areas.
It is also important to note that Google Scholar can provide access to research from around the world. This is particularly useful for understanding the role of telemedicine in rural healthcare in different contexts. For example, the challenges faced by rural communities in the United States may be different from those in other parts of the world, and solutions that have worked in one context may not be applicable in another.
Telemedicine: A Boon for Rural Patients in America
In the United States, the importance of telemedicine in rural health care has been recognized and is growing steadily. Telemedicine rural practices have immensely contributed in transforming the rural healthcare scenario, ensuring the delivery of primary care services to rural communities that previously had limited or no access to healthcare.
According to a study published in the Journal of Rural Health, telehealth services have the potential to improve access to primary care for more than 2 million rural patients in the United States. It also states that telemedicine can reduce travel time for rural patients by an average of 49 minutes per visit.
Virtual health technology, another facet of telemedicine, plays a significant role in monitoring and managing the health of rural patients with chronic conditions. With the help of health technology, healthcare providers can monitor the vital statistics of their rural patients remotely and make informed decisions about their care.
For example, remote patient monitoring devices can alert healthcare providers to changes in a patient’s condition, enabling early intervention that can prevent hospitalization. This not only improves patient outcomes, but also reduces healthcare costs.
Moreover, the advent of the telehealth resource center in the United States has shown promising results in advancing healthcare in rural communities. These centers provide valuable resources and technical assistance to healthcare providers and organizations that are implementing telehealth programs.
Conclusion: A Promising Future for Rural Health
The evolution of telemedicine has certainly shed light on the potential for its role to be instrumental in improving rural healthcare access. As we continue to navigate the post-Covid landscape, the importance of telemedicine has been underscored in ensuring that rural communities are not left behind in accessing vital healthcare services.
The application of virtual health technology, the increasing body of research surrounding telemedicine, and the establishment of telehealth resource centers all signal promising advancements in telemedicine rural practices. Furthermore, these developments have the potential to transform the face of rural healthcare in the United States and beyond.
However, while the advancements in telemedicine are promising, we must remember that rural health care is a complex issue that cannot be solved by telemedicine alone. It will take a comprehensive strategy that addresses not only healthcare delivery but also workforce shortages, transportation issues, and preventative care to truly make a difference.
Nonetheless, as we continue to innovate and adapt, there is hope that the gap in healthcare access between rural and urban areas will continue to close. Telemedicine, with its potential to bring healthcare to the doorsteps of rural patients, undoubtedly remains a key component of this journey.